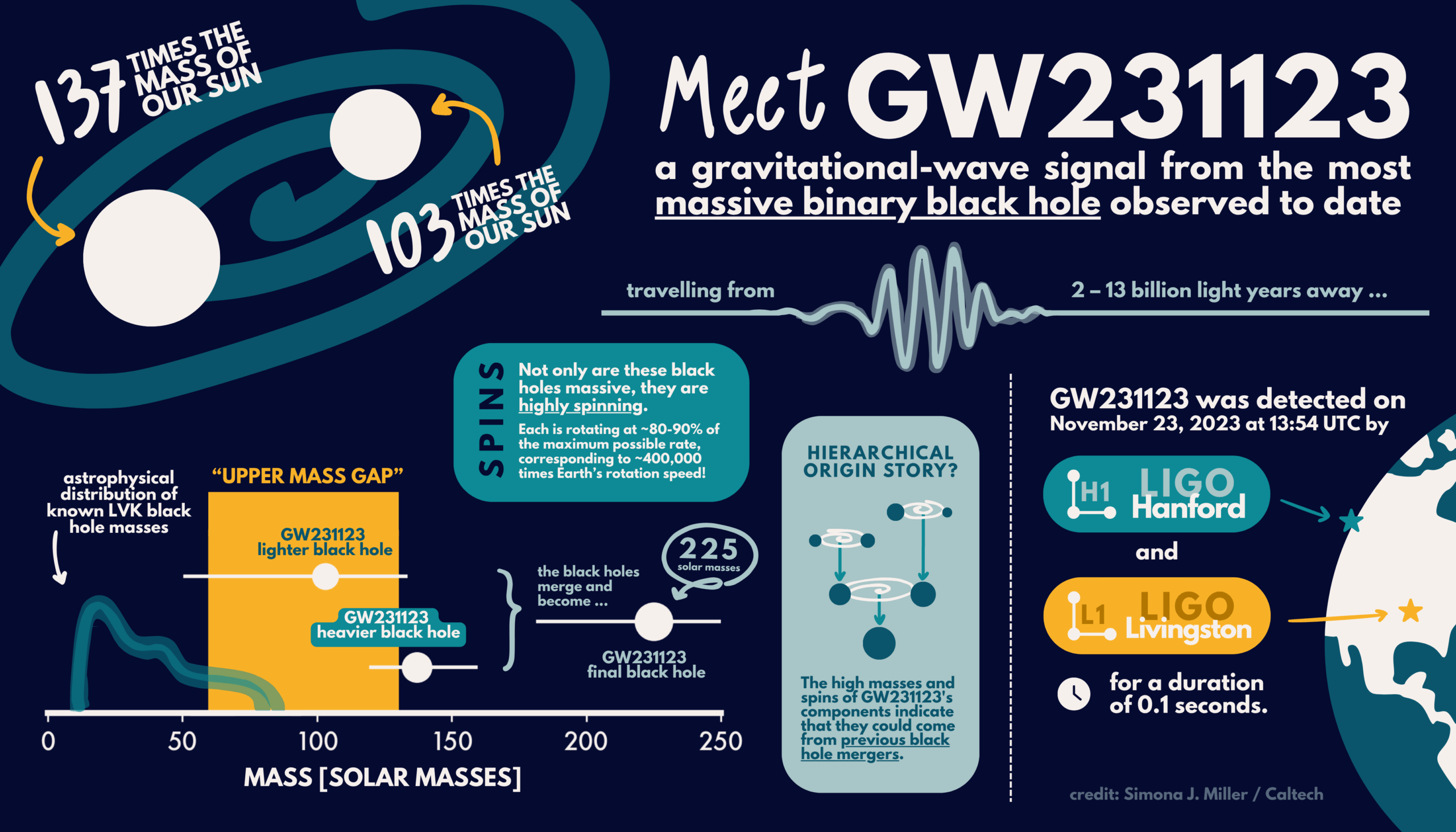
The LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA (LVK) Collaboration has detected the merger of the most massive black holes ever observed with gravitational waves, using the US National Science Foundation-funded (NSF) LIGO Hanford and Livingston Observatories. The merger produced a final black hole more than 225 times the mass of our Sun. The signal, designated GW231123, was observed during the fourth observing run (O4) of the LVK network on November 23, 2023.
The two black holes that merged were approximately 100 and 140 times the mass of the Sun. In addition to their high masses they are also rapidly spinning, making this a uniquely challenging signal to interpret and suggesting the possibility of a complex formation history.
“This is the most massive black hole binary we’ve observed through gravitational waves, and it presents a real challenge to our understanding of black hole formation,” says Professor Mark Hannam, from Cardiff University and a member of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration. “Black holes this massive are forbidden through standard stellar evolution models. One possibility is that the two black holes in this binary formed through earlier mergers of smaller black holes.”
To date, approximately 300 black-hole mergers have been observed through gravitational waves, including candidates identified in the ongoing O4 run. Until now the most massive confirmed black-hole binary was the source of GW190521, with a much smaller total mass of “only” 140 times that of the Sun.
For more details read the full news release and the GW231123 detection page.